NOTEYou should read this post.
I try to explain in a simple way how text-to-image models generate images.
This help you to understand how the things work in ComfyUI.
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Pony Diffusion
- Checkpoints
- Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs)
- Contrastive Language–Image Pretraining (CLIP)
- ComfyUI
Pony Diffusion
is a base model (checkpoint) fine-tuned from Stable Diffusion to generate both SFW and NSFW images.
Checkpoints
Checkpoint (base model) is file that includes all the information needed to load and use.
So, it has the ability to generate images based on text prompts.
A checkpoint includes the trained components along with their configurations, such as:
- Latent Diffusion Model
- VAE (Variational Autoencoder)
- CLIP (Contrastive Language–Image Pretraining)
Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs)
To understand how Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) generate images, we need to break the process down into two key concepts:
- Diffusion Process
- Latent Space
Diffusion Process
Machine learning method used in generative models to generate data.
It transforming simple random noise, through a series of iterative steps, into data (images).
The diffusion process involves two phases.
Forward Diffusion Process
In this phase, random noise is progressively added to an image step by step until it becomes completely unrecognizable (forward diffusion process).
During this process, neural networks are trained to predict the noise from the original image.

Reverse Diffusion Process
The trained Neural networks predict and remove the noise added during the forward process.
Starting with a noisy image, the model removes noise step by step to reconstruct a clear image.
That’s why this process is called the reverse diffusion process.

The model tries to recover the original image it was trained on by systematically subtracting the noise.
Latent Space and VAE
When working with images, each pixel is represented as a number, encoding information.
For example, a 1024x1024 color image results in a 1024x1024x3 matrix of numbers, or 3,145,728 pixels to process for just one image.
Training on millions of such large images would take months or years with current hardware.
To address this, LDMs operate in a compressed “latent space” (reduced images) rather than directly on the raw pixel data.
What is Latent Space?
Latent space is a simplified version of the image that retains its essential features while discarding irrelevant details, such as background noise.
For example, in an image of a cat, latent space focuses on the cat’s shape and form rather than every individual pixel.
Variational Autoencoder (VAE)
Latent space is generated using a variational autoencoder. VAE is a neural network with an encoder-decoder architecture.
- The encoder compresses the image into its latent representation.
- The decoder can reconstruct the image from this representation.

Why Use Latent Space?
Working in latent space significantly reduces the computational burden, making the process faster and more efficient.
This optimization allows models like Stable Diffusion to generate high-quality images in seconds.
Contrastive Language–Image Pretraining (CLIP)
CLIP is a Neural Network model that links images and text by learning what parts of images correspond to certain words.
CLIP understands what you mean when you describe an image (e.g., “picture of a cat”) and helps guide the LDM to create an image that matches that description.
It’s like a translator between your text input and the model.
How CLIP works
- Text Tokenization: The input text (e.g., “picture of a cat”) is tokenized and converted into a text vector.
- Guiding Image Generation: This vector acts as a guide, influencing the image generation model to create an image that aligns with the text.

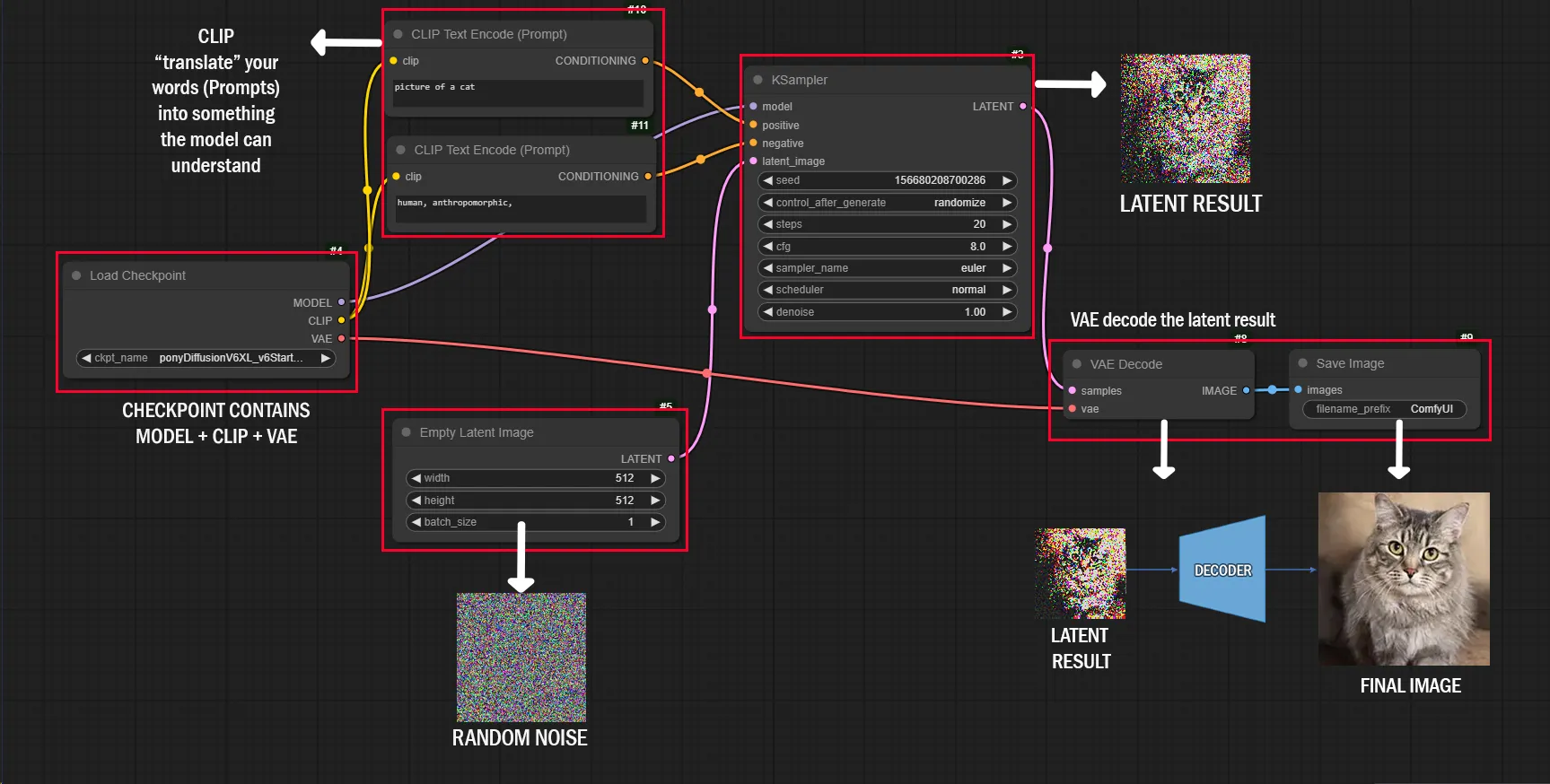
ComfyUI
How Things Work Together
CLIP
You type a description, e.g., “picture of a cat”
CLIP processes this text and translates it into a representation that matches the intended image.
This acts as a “guide” for the LDM.LDM
Begins with random noise in the latent space (compressed form).
It iteratively refines this noise into a latent image by following two signals:
CLIP guidance: Ensures the image aligns with the text.
Model knowledge: Provides artistic and structural details.VAE
Once the LDM finishes creating the latent image, the VAE decodes it into a high-resolution image.
Final Analogy
CLIP is like a translator who tells the artist what you want.
LDM is the artist sketching and refining the idea in a draft format.
VAE is the printer that turns the draft into a detailed, polished artwork.